A CDP - or Customer Data Platform - is a packaged SaaS data and marketing platform that collects first-party customer data from all your different systems and unifies that data to create a single 360 degree view of each customer. It does this by merging customer or prospect data from all those different sources against a unique identifier.
CDPs also allow you to use this data for marketing automation, personalization and optimization, so you can ensure you’re sending customers and visitors the right message, at the right time, and the right place. CDPs also give you deep analytical insights from the data collected from all your different systems, so that you can optimize your marketing efforts.
Some of the data CDPs collect about customers can include:
- Purchase history
- Browsing history
- Demographics
- Geographic data
- Device data
- Customer service history
- Email behaviour
- Behaviour on apps
- Propensity to purchase
- Customer lifetime value
- Next best product recommendation
- Likelihood to churn
CDP Features
Data Collection
CDPs collect data from a number of different sources, usually via connectors, APIs, event trackers like JavaScript tags and SDKs, server-to-server integrations and manual imports.
Identity Resolution & Profile Unification
When a CDP receives this data it looks for whether a profile for that user already exists by looking for the same device or identifier.
CDP’s build and maintain graphs of user-profiles and their identifiers, like their device ID, PII, cookies, IDFA, etc. This ensures all activity can be mapped back to a single user ID.
If the CDP matches an identifier with an existing profile, it will map the activity to that profile, otherwise it will create a new one. This gives users a complete, 360 degree view of every visitor and all their touchpoints.
Data Cleaning
Because you’re collecting data from different sources it often enters a CDP in different formats, so CDPs also transform the data into a common format, remove any redundancies and transform it into the CDP’s schema. Examples of this could include turning the IP address into a geolocation, extracting IDs from cookies or taking device types from the user agent string.
Segmentation
One of the most important features of any CDP is the ability to segment audiences into custom segments that you can then use to personalize experiences and run targeted messaging or campaigns across any of your channels.
You can segment by any number of factors, such as purchases, spending level, product interests, personas, pages visited, channels used, estimated future value and more, and can be segmented and exported for ad targeting in your ad platforms like Facebook and Google Ads.
Advanced Reporting
Because a CDP is collecting so much data from so many places they can produce advanced analytics reports that provide additional insights into audience behaviour and engagement that you won’t be able to get from your siloed data alone.
These reports can then be used to improve campaign performance and increase website conversions.
Activation
Some CDPs are known as ‘Smart Hub CDPs’, which come with the technology that allows you to use that data to run personalization on your different channels. Not all CDPs have this feature, but regardless, all CDPs should contain an activation layer that allows you to put the data to use thorough personalized content and experimentation with other channels, while ensuring it’s kept up to date.
Predictive Analytics
The best CDPs out there have machine learning / A.I. capabilities to analyze the data and make predictions from it, such as what someone’s customer lifetime value will be, or what products they’re likely to be interested in next, as well as what the next best actions for visitors are based on live customer and visitor context.
CDP Benefits
Reduces Data Silos
Organizations typically have a lot of software not only in their marketing stack but across the entire business that collects customer data. These apps usually accumulate their own customer data, which causes organizations to end up with a lot of decentralized data silos that make marketing efforts harder. Organizations who have siloed customer data have to spend a lot of time and effort pulling information bit by bit from different data sources, that are usually owned by different teams, and in different formats. This then makes taking action with that data and providing visitors with 1:1 experiences nearly impossible, and makes it nearly impossible to have a deep, holistic understanding of their customers.
That’s where a CDP comes in. CDPs help organizations unify data from disparate sources into one place, making it accurate, accessible and more usable. CDPs reduce IT bottlenecks and give access to the data to marketing, customer service teams and business intelligence.
Collect First Party Data / Reduce Effects of Third Party Data Loss
A lot of apps out there collect third party data - data that’s collected and owned by another app and is separate from your relationship with your audience.
CDPs collect first party data - data that’s collected directly from your audience, using your own channels, via pixels and other tracking tools. First party is best since it comes directly from your audience and reflects the most accurate information.
Complete customer profiles
CDPs allow you to build a complete, holistic profile of each customer, giving you a 360 degree view into them. This is super important in marketing today since customers want to have personalized and 1:1 experiences, and in order to do that you need to know them well and to be able to pull this data from one place.
By capturing data from all the different apps, platforms and channels your customers interact with, both online and office, you can build a complete view of them that allows you to know them on a deep level and provide them with personalized experiences no matter what channel they’re using to interact with your brand. Whether that’s browsing the website or phoning the call centre.
Unified cross-channel marketing
CDPs allow you to target visitors across any channels with relevant content. Most of the best CDPs out there allow marketing apps like personalization and marketing automation to access the CDP to present personalized content across any channels. More personalized content and offers means customers spend more, and have a more positive experience with your brand.
Advanced Analytics For Optimization
CDPs give you advanced analytics since they collect data from all your channels that you can use to make smarter business and marketing decisions. You can use that data for identifying new and high-value segments, personalizing in real-time, feeding machine learning platforms, optimizing campaigns, predicting customer behaviour and willingness to spend.
Increased Revenue
CDPs can increase your company revenue by allowing you to target visitors and customers more intelligently. By having a deeper understanding of who your customers are, what their influences are, what their interests are, and how they shop and spend, you can target people with the right content, on the right channel, at the right time, and increase their likelihood of buying, as well as how much they spend and what they purchase.
CDPs & Data Privacy
Consumers have become much more privacy and data conscious over the past few years and laws and regulations, as well as technology updates have supported the movement to give customers and visitors more control over what information is collected about them.
Laws and regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have forced organizations to ensure that they’re compliant with data protection laws, giving massive fines to businesses who don’t adhere. At the same time, tech updates such as Apple’s iOS 14 update have made it more difficult for marketers to target their audiences effectively.
Thankfully a CDP can help businesses by making it easier for them to monitor their customer data by centralizing customer data to have in one place. To comply with privacy laws businesses need to be transparent about what information is collected about customers and how it’s collected. Visitors can request a copy of their data at any moment, or request that their data be deleted, so having all their data in one place solves this problem by making that process a breeze.
CDPs also make it easier for businesses to control the types of and amounts of data that they’re collecting about their audiences, allowing businesses to completely anonymize or not collect certain data if they can’t in order to adhere to privacy regulations.
CDPs vs Other Systems
A CDP may sound similar to other platforms and tools in your stack, for example you might be thinking that it sounds similar to what your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system already does for you, or your Data Management Platform (DMP). While CDPs share many of the same qualities as these other platforms, they’re actually quite different.
CDPs vs CRMs
Similarities:
- CDPs and CRMs both collect customer data stored against a customer profile
Differences:
- CDP collect customer data across all applications (i.e. visitor behaviour on a website), whereas CRMs do not
- CDPs collect data about anonymous visitors, CRMs do not
- CDPs collect data from offline channels, CRMs do not
- CDPs allow you to use the data to personalize experiences, CRMs do not
- CDPs provide advanced reporting and analytics, CRMs do not
- CDPs analyze lifetime customer behaviour and customer journeys, CRMs do not
CDPs vs DMPs
Similarities:
- Both collect customer data
Differences:
- CDPs collect PII like names, addresses, emails, etc. Whereas DMPs work with anonymous information like IP addresses, device IDs and cookies
- DMPs are used for improving ad targeting, whereas the data from CDPs is used for all types of marketing activities
- DMPs retain data short term to improve ad targeting, whereas CDPs retain long-term data to build deep, holistic customer profiles
- DMPs collect third-party data whereas CDPs collect mostly first-party data
CDP vs. marketing automation systems
Similarities:
- If a CDP is a smart-hub CDP, both CDPs and marketing automation tools can automate marketing activities
Differences:
- Marketing automation tools typically only use data from CRM systems, or behaviour on landing pages, whereas CDPs collect and use data from any channels
- Smart-hub CDPs can deliver personalized experiences in real-time on any channels, whereas marketing automation platforms typically only do so via email and landing pages
- CDPs are built to provide actionable insights to marketers that can be used for marketing and targeting across any channels, whereas marketing automation tools typically only drive campaigns without providing deep insights
CDP vs Data Warehouses
Similarities:
- Both data warehouses and CDPs store data
- Both are used for reporting and analysis
- Both are used to create a centralized area for data storage
Differences:
- Data warehouses typically store all corporate data, whereas CDP’s only store customer data
- CDPs are built for marketers, whereas data warehouses are built for business intelligence
- CDPs include cross-channel identity resolution, where as data warehouses don’t
- CDPs provide real-time updates, whereas data warehouses don’t
- Data warehouses typically only store structured data, whereas CDPs can store unstructured, semi-structured and structured data
CDP vs Data Lakes
Similarities:
- Both store data
Differences:
- Data lakes store raw and unprocessed data in its original format, whereas CDPs store cleaned and transformed data
History of CDPs
There is some contention around when the term Customer Data Platform was first used. Some sources say 2010, others say 2013, regardless, we know it was roughly around this period. According to Google Trends, the term first had interest even way back in 2004, although the interest didn’t start ramping up until around 2015.
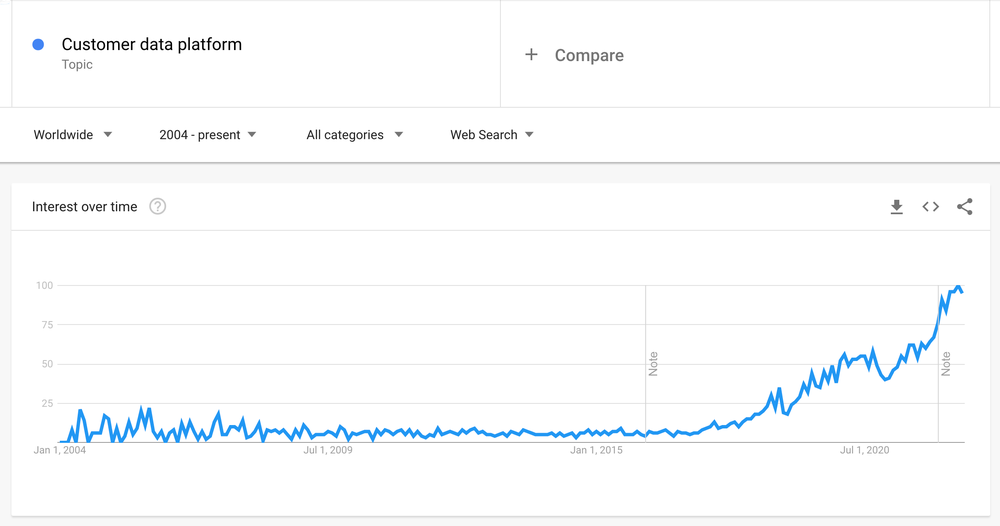
The term was used to describe software that could build a single customer view by collecting a customer’s data into one platform.
CRMs have been used since the 90s to collect customer data that can be used for managing a company’s interactions with their customers, however as marketing technologies evolved and businesses bought more platforms that collected customer data, data became siloed. CRMs weren’t set up to be a centralized point of customer data or to share that data between other platforms like marketing automation platforms. DMPs were born in the 2000s to inform and feed paid media campaigns and were used by advertisers, however these platforms still weren’t set up to be a central location for all customer data.
CDPs were then born to meet the need for a central point of data that can share that data with other applications and systems, and were initially used to power other softwares for marketing, like personalization and marketing automation tools. They’ve since evolved to become their own established softwares and some analytics and tag management providers even adapted their softwares into similar solutions.
By 2016 these softwares had started the CDP industry, which grew quickly as marketers needed something better than data lakes and DMPs for managing their customer data and sending it easily between systems. 2016 was also the year that they first appeared on Gartner, and this was also the year that the Customer Data Platform Institute was formed.
Today CDPs are an established software recognized by Gartner and Forrester, and predicted to grow at 25.4%, to USD 6.94 billion from 2022 to 2029 according to Fortune Business Insights.
Advanced CDPs now feature A.I. and machine learning capabilities that allow predictive modelling, as well as advanced segmentation, analytics and customer scoring and grading. They also help businesses to manage customer data to stay in compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR, offering features like the right to be forgotten.
Choosing A CDP
CDPs can come with all sorts of different functionalities and they’re not all created equally.
At the end of the day you need to choose a CDP that contains features that will be the most valuable for your business.
Most CDPs contain these features:
- Ability to collect first party data from both online and offline channels
- Audience segmentation to inform marketing efforts and to use with personalization
- Single, 360 degree customer views
By far the best CDPs with the most bang for your buck are Smart Hub CDPs. Smart Hub CDPs have been described as ‘the marketer’s dream’, as they contain a CDP, along with built in personalization and execution features that are very much plug and play, all from the one interface.
These CDPs contain A.I. and decision modeling functionality that can target users on any channel, based on their behaviour, data or any other information you’ve collected about your users in the CDP.
Smart hub CDPs also contain advanced analytics and reporting functionality, as well as advanced A/B testing and experimentation, so you have everything you need to provide the optimal customer experience and reach your marketing goals in the one place.
What's The Best Smart Hub CDP?
Sitecore CDP is the best smart hub CDP in terms of value and bang for your buck.
With Sitecore CDP you get a best in breed CDP as well as an advanced personalization platform that includes:
- A comprehensive, 360 degree, holistic profile of all your customers that consolidates data from online and offline channels.
- Real-time segmentation that uses live audiences to track customer behaviour across all channels.
- Data consolidation & cleaning to combine all your customer data from all your sources, channels and platforms in one place.
- Advanced audience retargeting and analytics to convert more customers with precise retargeting campaigns utilizing first party data.
- Data security and protection, so your customers can rest assured that their data is secure.
- Real-time Personalization that uses machine learning to predict the next best scenario for each customer based on real-time behaviour and business context.
- Omni-channel personalization so you can speak 1:1 with your audience on any channel.
- A/B testing & experimentation that automates the testing process.
- Personalization and testing analytics that allow you to measure the impact against business KPIs
- Intuitive interface that makes personalization easy.



