Restore The SQL Database From Multiple Backup Files
Learn how to restore the SQL database from multiple backup (BAK) files in SQL Server Management Studio
Learn how to restore the SQL database from multiple backup (BAK) files in SQL Server Management Studio
A file with a .bak extension is usually a backup file that is used by different software tools to store backups of data. From a database perspective, a BAK file is used by Microsoft SQL Server for storing the contents of a database. All the data and files associated with the database are stored in this file format to be retrieved in case the database becomes corrupt or invalid for any reason. The backup files can be stored and indexed on other servers for safety purposes. Several applications can create BAK files such as SQL Server Management Studio, Transact-SQL, and Windows PowerShell.
Search your local SQL server installation directory and locate the Backup directory, which is usually C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL. Paste the files inside the mentioned directory and proceed with the next step.
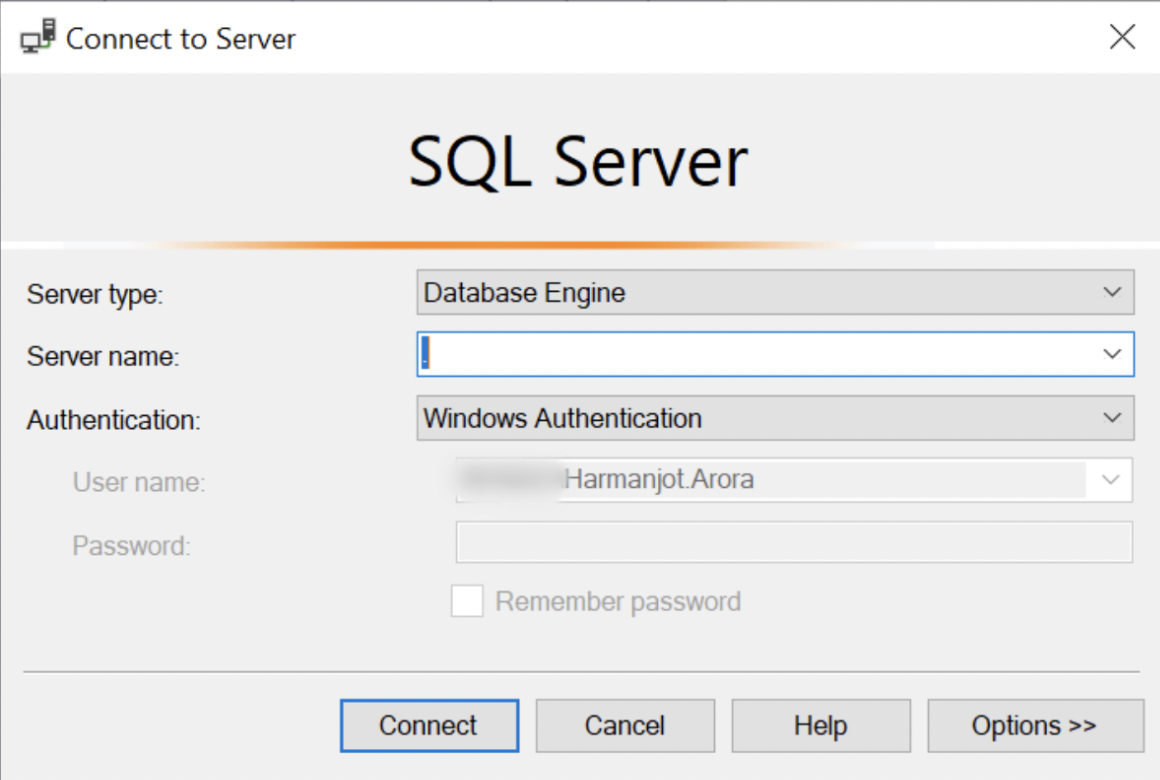
Open SSMS and access the database engine with the default Windows authentication (or from the connection that you want to access) and click Connect.
Select the Databases node, right click and click on Restore Database.

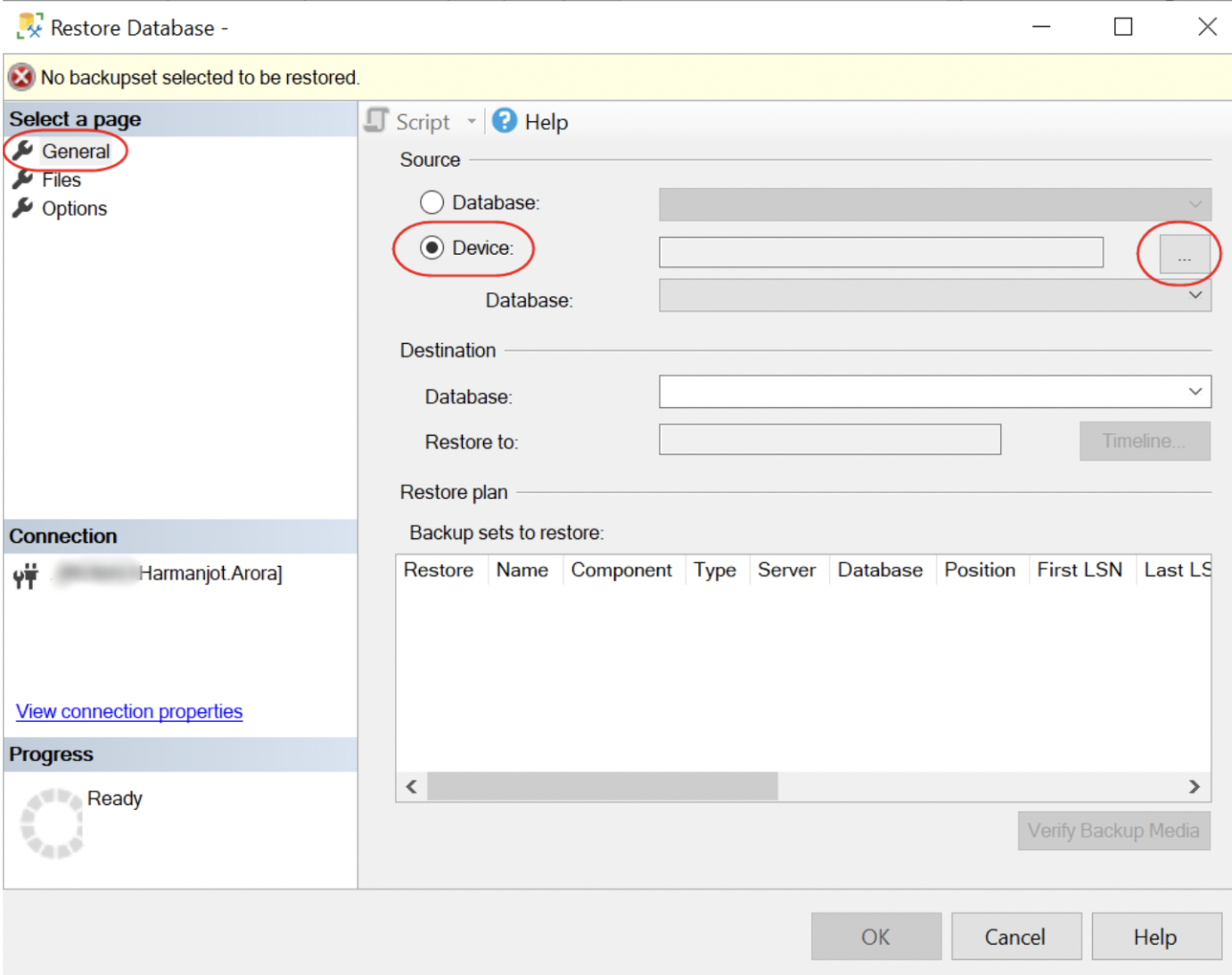
This will open the restoration dialog. In this dialog, select the General tab and set the source to Device, and click on the ellipsis (...).
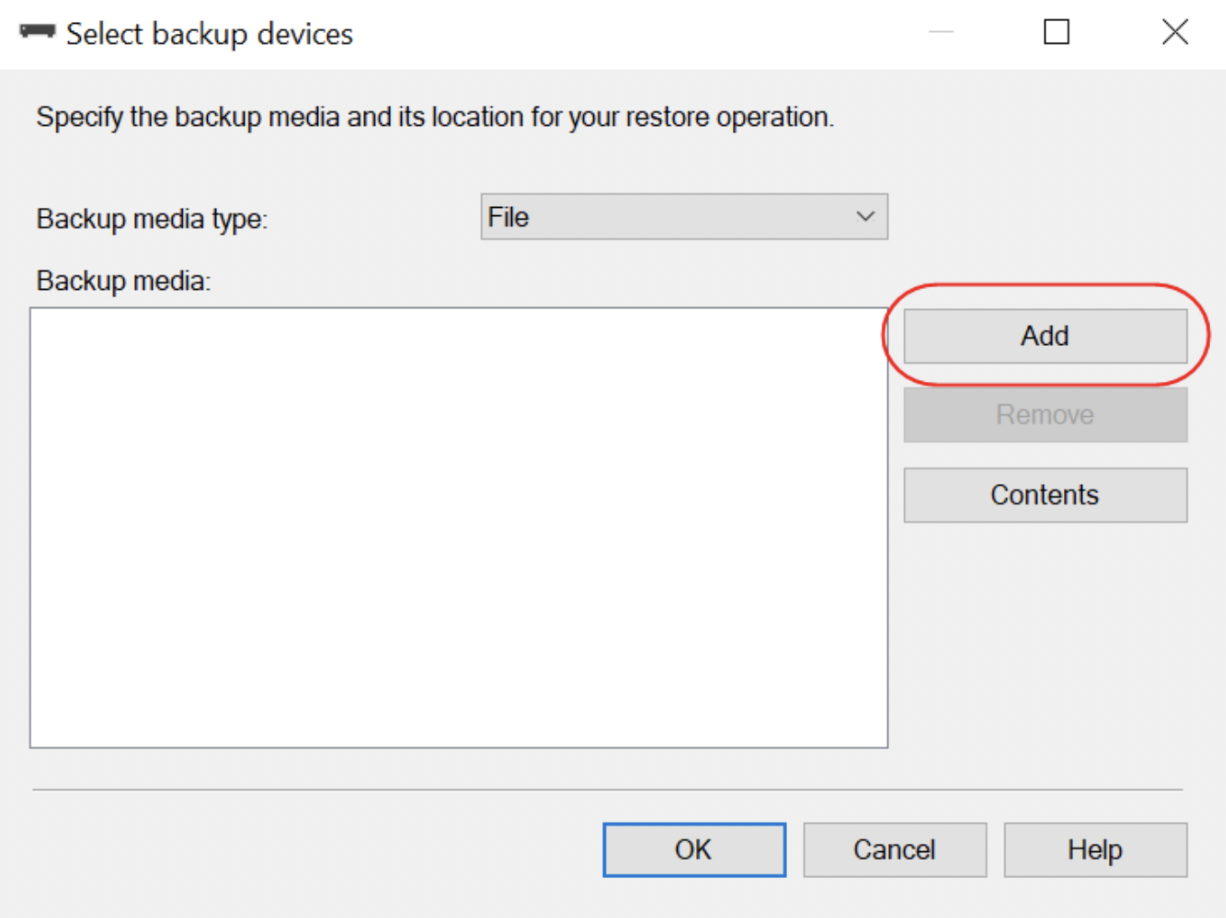
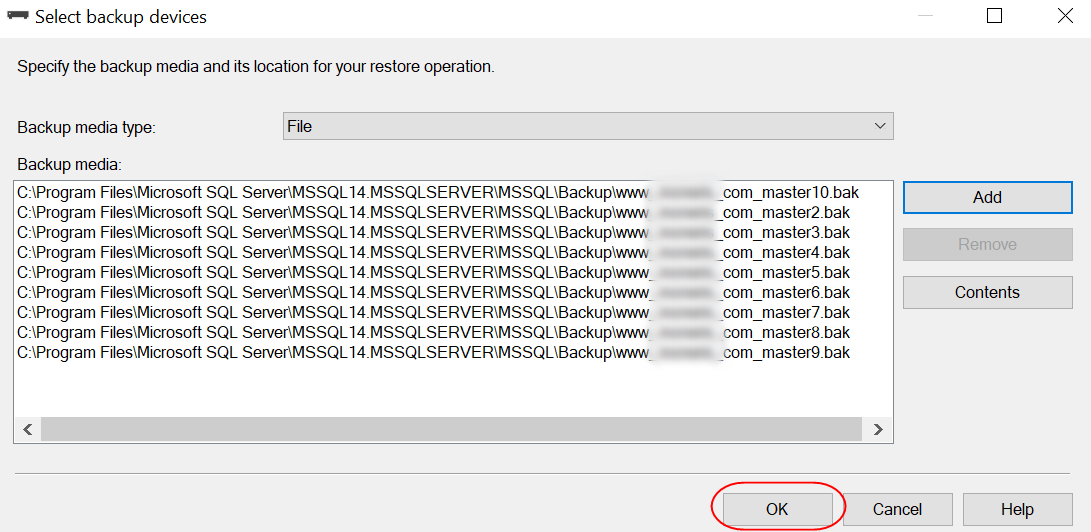
This will open the Select backup devices dialog, here you will be able to select the .bak files from the directory mentioned on the first step when you click on Add.
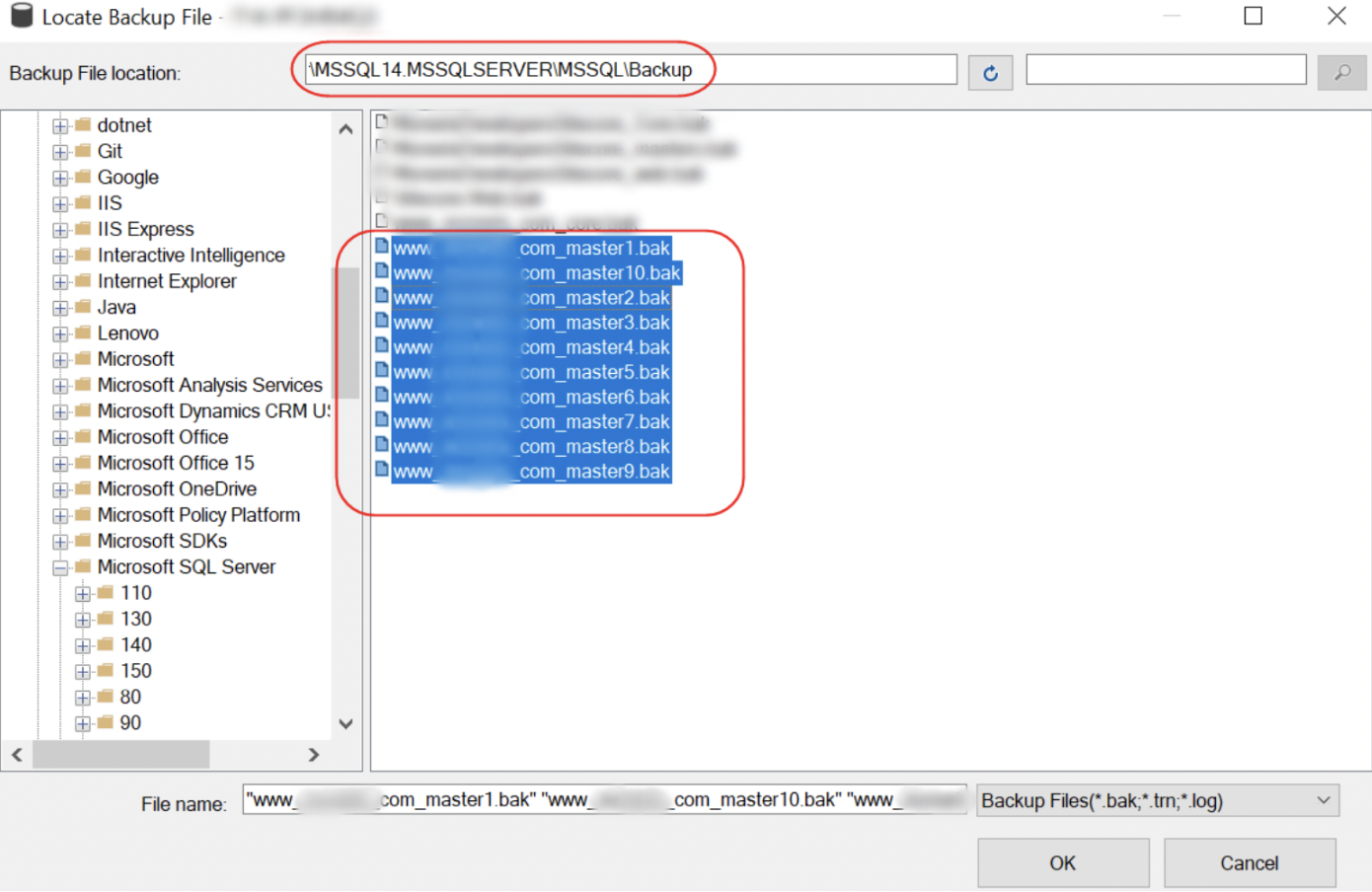
Select the files and click OK.
This will add the files to the backup devices, and click on OK.
Once you click on OK, the database(s) stored on the bak files will be listed and you will need to select which of them (if more than one) you want to restore.
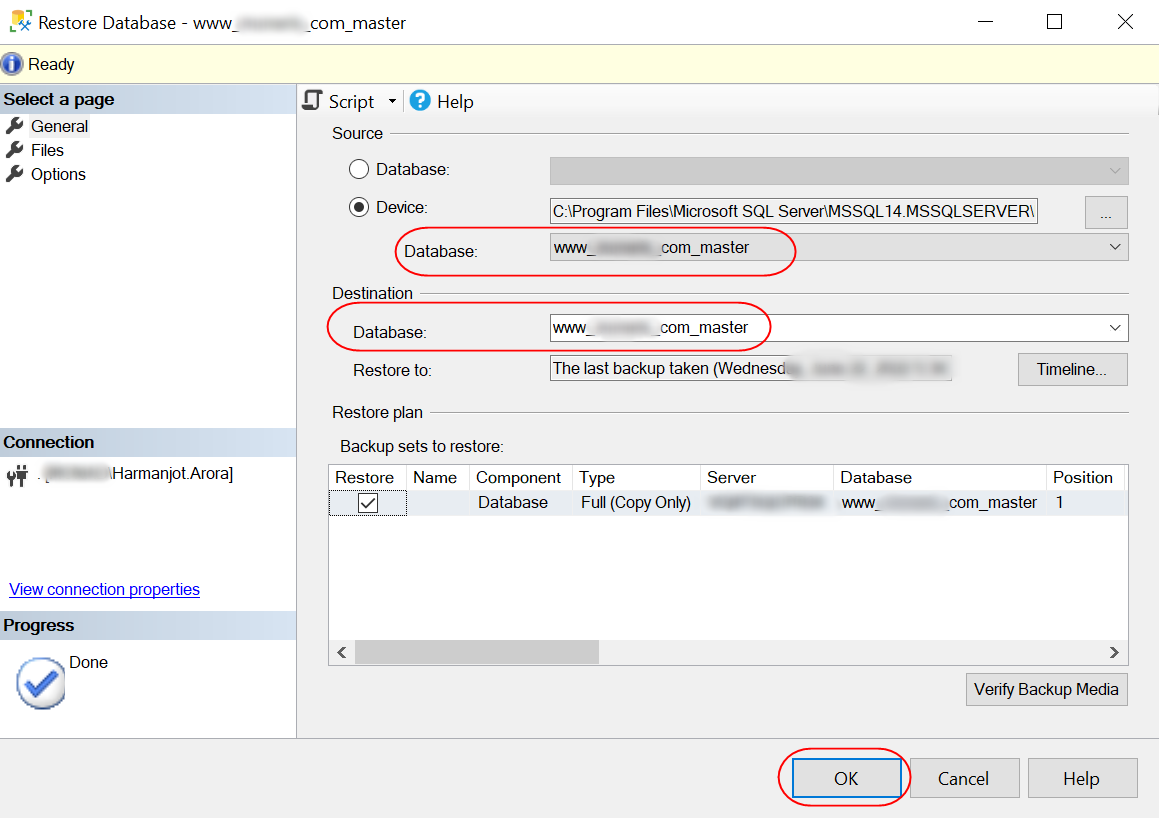
Once you click on OK, the restoration process will start and you will find your new databases restored on your server.
Start typing to search...